The Rising Cost of Healthcare: A Threat to Your Health and Financial Security
Introduction
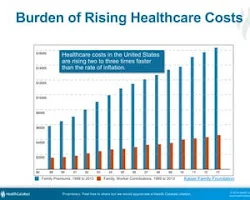
In today's world, the rising cost of healthcare has become a significant concern for individuals and families alike. The escalating expenses associated with medical treatments, medications, and insurance premiums pose a threat not only to our health but also to our financial security. This technical paper aims to explore the reasons behind the increasing healthcare costs, highlight their impact on individuals and the economy, and provide potential solutions to mitigate this growing problem.
The Alarming Rise of Healthcare Costs
Understanding the Factors Driving the Cost Surge
Healthcare costs have been steadily rising over the years, and it's crucial to comprehend the various factors contributing to this surge. By examining these elements, we can gain a better understanding of the challenges faced by individuals seeking medical assistance.
Medical Technological Advancements and Innovation
The continuous advancements in medical technology have undoubtedly improved patient care and outcomes. However, these innovations come at a high price. Cutting-edge treatments, diagnostic tools, and pharmaceuticals often require significant investments in research, development, and production, which ultimately drive up healthcare costs.
For example, the cost of cancer drugs has increased by more than 1,000% in the past 20 years. This is due to a number of factors, including the high cost of research and development, the limited number of manufacturers, and the lack of competition.
Administrative Complexity and Overhead Expenses
The complexity of healthcare systems, including insurance claims, billing procedures, and regulatory compliance, adds substantial administrative costs to the overall healthcare expenditure. The intricate web of bureaucracy and paperwork can burden healthcare providers, resulting in increased overhead expenses that ultimately trickle down to patients.
For example, the average administrative cost for a physician's office is now over $200,000 per year. This is due to the increasing number of regulations governing healthcare, the need to comply with insurance requirements, and the use of electronic health records.
Aging Population and Chronic Diseases
The aging population, coupled with the rise in chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and cancer, places an enormous burden on the healthcare system. Older adults often require more extensive medical care and long-term management of their conditions, leading to higher costs for both individuals and society as a whole.
The United States has the oldest population in the world, with a median age of 38.2 years. This number is expected to continue to rise in the coming years, as the baby boomer generation ages. The aging population will place a significant strain on the healthcare system, as older adults are more likely to need medical care and have chronic diseases.
Prescription Drug Prices
Pharmaceutical expenses constitute a significant portion of healthcare costs. The soaring prices of prescription drugs, particularly for life-saving medications, have drawn considerable attention and sparked debates about affordability and accessibility. Factors such as research and development costs, marketing expenditures, and the patent system contribute to the high prices of prescription medications.
The average price of a prescription drug in the United States is now over $1,000. This is significantly higher than the prices of prescription drugs in other developed countries. The high cost of prescription drugs is a major barrier to access for many people, and it can lead to financial hardship for those who do have access.
Provider Consolidation and Lack of Competition
The consolidation of healthcare providers, including hospitals and medical practices, has led to decreased competition in certain regions. This lack of competition allows providers to exert greater control over pricing, leading to inflated healthcare costs.
For example, the number of hospitals in the United States has declined by over 20% since 1980. This consolidation has led to higher prices for hospital services, as providers are no longer forced to compete for patients.
The Impact on Health and Financial Security
The rising cost of healthcare has profound implications for both our health and financial security. Let's delve into the consequences of this alarming trend.
Limited Access to Medical Care
As healthcare costs continue to rise, individuals with limited financial means may struggle to access necessary medical care. The lack of affordable options and insurance coverage can result in delayed or inadequate treatment, leading to worsened health outcomes.
A study by the Kaiser Family Foundation found that nearly one in five adults (19%) did not receive needed medical care in the past year due to cost. This number is even higher for low-income adults, with nearly half (47%) reporting that they did not receive needed medical care due to cost.
Increased Financial Burden on Individuals and Families
Skyrocketing healthcare costs can place a significant financial burden on individuals and families. High insurance premiums, copayments, deductibles, and out-of-pocket expenses can quickly accumulate, causing financial strain and potentially leading to debt or bankruptcy.
A study by the Urban Institute found that the average household with health insurance spends nearly $4,000 per year on out-of-pocket expenses. This number is even higher for households with high-deductible plans, which are now the most common type of health insurance plan in the United States.
Adverse Effect on Small Businesses
Small businesses often struggle to provide comprehensive healthcare coverage for their employees due to the exorbitant costs involved. This can hinder their ability to attract and retain talented individuals, thus affecting their competitiveness and overall growth.
A study by the National Federation of Independent Business found that nearly half of small businesses (48%) do not offer health insurance to their employees. This is due to the high cost of health insurance, which has increased by more than 200% in the past 20 years.
Economic Consequences
The escalating cost of healthcare also has broader economic implications. It diverts a substantial portion of household income away from other sectors, limiting consumer spending and reducing economic growth. Additionally, rising healthcare costs can strain government budgets and lead to higher taxes or decreased funding for other essential services.
A study by the Congressional Budget Office found that the cost of healthcare is expected to grow by more than 5% per year over the next decade. This growth will put a significant strain on the federal budget, as the government is the largest payer for healthcare in the United States.
Potential Solutions to Mitigate Healthcare Costs
Addressing the issue of rising healthcare costs requires a multi-faceted approach involving various stakeholders, including policymakers, healthcare providers, insurers, and individuals themselves. Here are potential solutions that could help alleviate the burden:
Promoting Preventive Care and Wellness Programs
Emphasizing preventive care and wellness programs can reduce the incidence and progression of chronic diseases, ultimately leading to lower healthcare costs. Encouraging individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles and providing incentives for preventive screenings can result in long-term cost savings.
Enhancing Price Transparency
Improving price transparency in the healthcare system empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their healthcare options. Clear and accessible information regarding the cost of treatments, procedures, and medications allows patients to compare prices and choose more cost-effective alternatives.
Embracing Technological Innovations
Harnessing the power of technology can drive efficiency and cost savings in healthcare. Electronic health records, telemedicine, and remote patient monitoring are just a few examples of innovations that can streamline healthcare delivery, reduce administrative costs, and improve access to care, especially in rural areas.
Encouraging Competition and Price Negotiations
Policymakers can promote competition among healthcare providers and insurers to drive down costs. Initiatives such as antitrust enforcement, increased price negotiations for prescription drugs, and the introduction of competitive bidding processes can help create a more affordable healthcare landscape.
Reevaluating Insurance Models
Exploring alternative insurance models, such as health savings accounts or value-based insurance design, can incentivize cost-conscious decision-making among individuals. These models promote greater transparency, cost-sharing, and aligning insurance coverage with value-based outcomes.
Conclusion
The rising cost of healthcare presents a significant threat to both our health and financial security. Understanding the factors driving this surge and its impact on individuals and the economy is crucial for finding viable solutions. By promoting preventive care, enhancing price transparency, embracing technology, encouraging competition, and exploring alternative insurance models, we can strive towards a more affordable and sustainable healthcare system. Addressing the rising cost of healthcare is essential for safeguarding our well-being and ensuring a healthier and financially secure future.
References:
- The Commonwealth Fund: https://www.commonwealthfund.org/
- The Kaiser Family Foundation: https://www.kff.org/
- The Urban Institute: https://www.urban.org/
- The Center for American Progress: https://www.americanprogress.org/















.png)
0 Comments